Professionals in graphic design and visual branding increasingly rely on powerful tools to bring concepts to life with stunning realism. Among these, Adobe Dimension stands out as a dedicated 3D compositing and rendering application that bridges the gap between 2D design workflows and immersive three-dimensional visuals. This software empowers creators to produce photorealistic product mockups, brand visualizations, and scene compositions without requiring advanced 3D modeling expertise. In the following comprehensive guide, we delve deeply into what makes Adobe Dimension an indispensable asset for modern designers.

Understanding Adobe Dimension: Core Concepts and Evolution
Adobe Dimension, originally launched as Project Felix in beta form, represents Adobe’s strategic entry into accessible 3D design tools tailored specifically for graphic designers rather than traditional 3D artists. Unlike complex programs such as Blender, Maya, or Cinema 4D that demand extensive training in polygonal modeling, rigging, and animation, Adobe Dimension prioritizes rapid compositing of pre-built 3D models with 2D graphics and environmental elements.
At its heart, the application excels in creating composite scenes where users import or select from extensive libraries of 3D assets, apply high-quality materials, position accurate lighting, and overlay custom decals, logos, or artwork. The result is a rendered image that mimics real-world photography, making it ideal for product visualization, packaging prototypes, and marketing materials. This approach democratizes 3D rendering by leveraging Adobe’s ray-tracing engine (formerly powered by partnerships with technology like NVIDIA Iray) to deliver realistic reflections, refractions, shadows, and global illumination.
Over the years, Adobe Dimension has evolved through regular updates, integrating deeper connections with other Creative Cloud applications. Designers can seamlessly pull vector graphics from Illustrator, raster images from Photoshop, and stock assets directly from Adobe Stock, ensuring workflow continuity. The software’s intuitive interface—divided into clear panels for scene management, properties, materials, and camera controls—reduces the learning curve significantly compared to industry-standard 3D suites.
One of the standout philosophical shifts introduced by Adobe Dimension is its focus on “match image” technology. This feature analyzes a background photograph and automatically adjusts the 3D scene’s lighting and perspective to blend perfectly, creating the illusion that the 3D object was photographed in the real environment. Such automation elevates output quality while minimizing manual tweaks, allowing creators to focus on artistic decisions rather than technical adjustments.
Key Applications and Practical Uses of Adobe Dimension
The versatility of Adobe Dimension extends across multiple creative industries, from consumer product branding to digital marketing and editorial design. Its applications revolve around producing high-fidelity visuals that communicate ideas convincingly to clients and audiences.
Crafting Professional 3D Visualizations
Central to Adobe Dimension‘s appeal is its robust support for building detailed 3D scenes from scratch or templates. Users access a vast library of parametric models—bottles, boxes, electronics, furniture, and abstract shapes—that can be scaled, rotated, and customized effortlessly. Combined with physically based materials (PBR) offering properties like metallicity, roughness, and emissive glow, these elements enable the creation of compelling product shots.
Navigation tools such as Orbit for rotating the view, Pan for shifting perspective, and Dolly for zooming provide precise control over composition. Designers often use these to explore multiple angles, ensuring the final render highlights key product features. This capability proves invaluable in e-commerce, where accurate 3D representations influence purchasing decisions by offering virtual “hands-on” experiences.
Moreover, Adobe Dimension supports importing custom 3D files in formats like OBJ, FBX, and STL, expanding possibilities for collaboration with modelers who create bespoke assets in specialized software.
Achieving Photorealistic Composite Imagery
Photorealism remains one of the most celebrated strengths of Adobe Dimension. By dragging vector artwork or raster labels onto 3D surfaces as decals, users can simulate printed packaging, branded merchandise, or labeled containers with remarkable accuracy. The software intelligently wraps graphics around curved surfaces, accounting for distortion and perspective.

Integration with Adobe ecosystem tools amplifies this process. For instance, preparing intricate label designs in Illustrator ensures vector sharpness at any resolution, while Photoshop edits allow for texture enhancements like embossing or metallic foils. The automatic environment matching further refines realism by syncing virtual lighting with real-world photos, producing shadows and reflections that align perfectly.
In practice, agencies use Adobe Dimension to pitch concepts before physical prototypes exist, saving substantial costs in manufacturing and photography. Beverage brands visualize new bottle designs, cosmetic companies preview packaging variants, and tech firms showcase devices in lifestyle settings—all rendered convincingly within hours.
Real-Time Preview and Efficient Rendering Workflow
The Render Preview mode offers interactive viewport feedback using a fast draft engine, allowing instant adjustments to materials, lights, or camera positions. This live iteration prevents wasteful final renders and encourages experimentation. Once satisfied, switching to high-quality mode engages the full ray-tracer for production outputs.
Adobe Dimension also supports background rendering, freeing the workstation for continued work. Outputs include layered PSD files preserving separate elements (ideal for post-production in Photoshop), transparent PNGs, or standard image formats. Advanced users appreciate bookmarking multiple camera views to batch-render variations efficiently.
Real-Time Ray Tracing and Export Flexibility
Powered by modern rendering technologies, Adobe Dimension delivers near-real-time feedback in the viewport for compatible hardware, particularly those with GPU acceleration. This interactivity enhances creative flow, as changes to lighting or materials update almost instantly.
Export options extend beyond static images to include 360-degree panoramas and web-friendly GLTF files for interactive online experiences, bridging traditional design with emerging AR/VR platforms.
Unleashing Creative Potential Without Boundaries
Ultimately, Adobe Dimension liberates designers from technical constraints, fostering bold experimentation. Whether conceptualizing surreal art installations, futuristic product concepts, or minimalist brand identities, the tool’s accessible yet powerful feature set encourages pushing creative limits.
Community-shared starter assets and templates further inspire innovation, while custom material creation allows for unique textures like wood grains, fabrics, or iridescent finishes. The combination of ease and depth ensures that both novice enthusiasts and seasoned professionals find ample room for expression.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mastering Adobe Dimension
Getting started with Adobe Dimension is straightforward, especially within the Adobe Creative Cloud ecosystem. Follow this detailed walkthrough to establish an effective workflow.
- Acquire Access: Subscribe to Adobe Creative Cloud, which includes Adobe Dimension in most plans. Ensure you have a legitimate license to unlock all features, including high-resolution rendering and cloud asset syncing.
- Launch and Setup: Open the application via the Creative Cloud desktop app. Upon first launch, explore starter scenes or create a new document with preferred canvas dimensions and background options.
- Build Your Scene: Import or select 3D models from the built-in library. Apply materials by dragging from the content panel, then position lights (sunlight, image-based, or point sources) for desired mood.
- Add Graphics: Drag SVG or AI files for decals, or use Photoshop layers for complex textures. Utilize the Magic Wand tool for quick environment matching if incorporating real photos.
- Refine Composition: Adjust camera properties, depth of field for focus effects, and environmental settings. Use Render Preview extensively to iterate.
- Finalize and Export: Render at full quality, choosing resolution up to 8K if needed. Export as PSD for layered editing, PNG for transparency, or other formats suitable for presentation or web use.
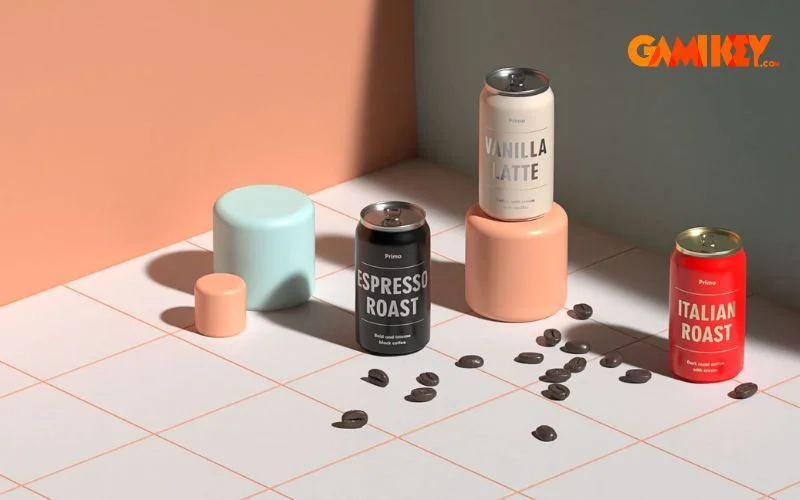

Advanced techniques include creating custom camera animations for turnaround views, utilizing substance materials for procedural textures, and leveraging actions for repetitive tasks. Regular practice with these elements will transform basic mockups into portfolio-worthy masterpieces.
In summary, Adobe Dimension redefines how graphic designers approach 3D visualization, offering a perfect balance of simplicity, integration, and professional-grade output. Its continued development within Creative Cloud ensures relevance in an increasingly visual digital landscape.
For further exploration of Adobe tools, consider related resources covering event conferences, management utilities, audio enhancements, and prototyping software.
